Virutalization
Hypervisor¶
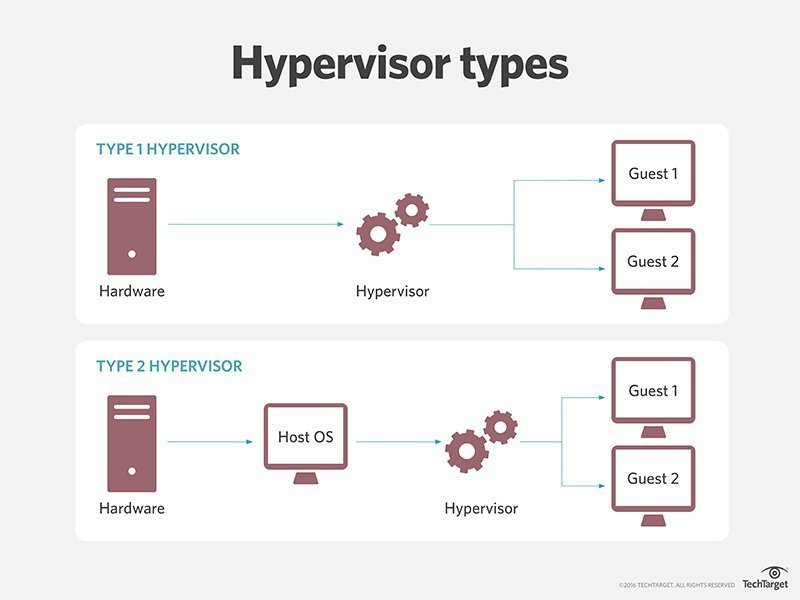
There are two types of hypervisors, type 1 and type 2. Type 1 hypervisors are services that have direct access to hardware. They do not rely on the host OS to execute instructions.
Type 2 hypervisors sit on top of the host OS which introduces a massive latency penalty.
KVM¶
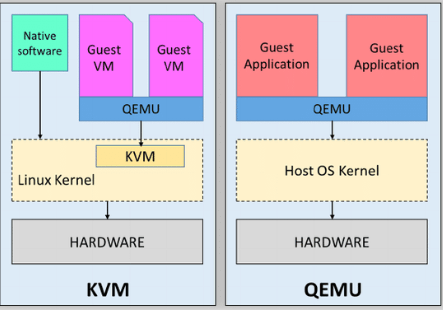
The Linux kernel provides a technology called the Kernel-based Virtual Machine. KVM makes use of the HVM (hardware virtual machine) extensions to give VMs direct access to host hardware. While KVM can be used by itself to launch virtual machines, it is not uncommon to see QEMU used in conjunction with KVM.
QEMU¶
The Quick Emulator is a full hardware emulator that allows you to run a VM for any kind of architecture, which is its main advantage over KVM. However, QEMU is much slower as instructions are typically not run natively on the host hardware but are rather dynamically translated. QEMU is also often more difficult to configure than KVM.
QEMU can work directly with KVM to allow acceleration on host platforms that support it. Lack of KVM support means QEMU must fully emulate the hardware which makes it much slower.
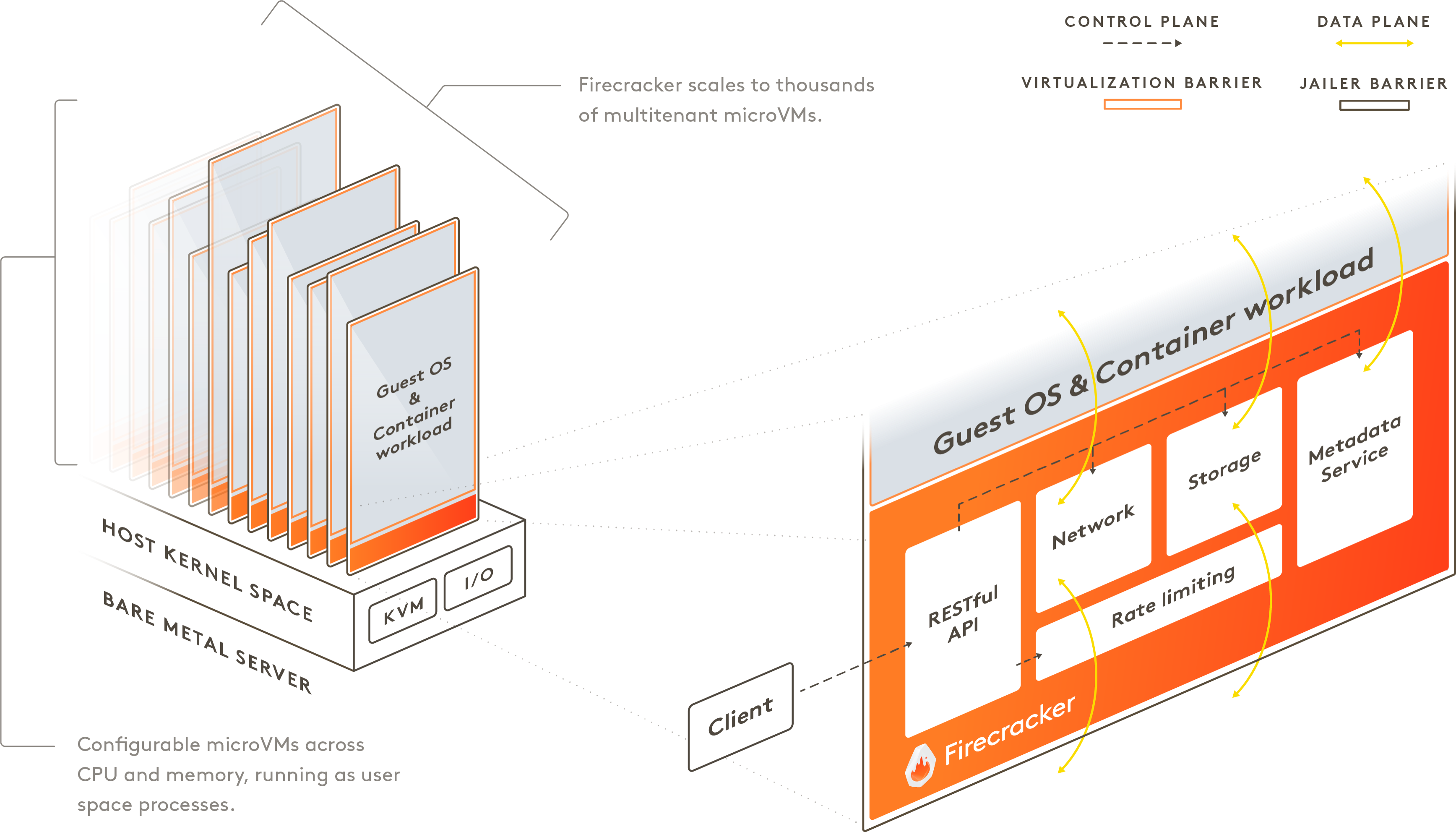
Firecracker¶
Firecracker is an alternative to QEMU that is built specifically for microVMs. It was created by AWS for the Lambda service.